Astronomers have discovered a galaxy 30 times larger than the Milky Way, a phenomenon they cannot explain (see photo).
Although giant radio galaxies are among the largest structures in the universe, they are not easily detected. Nevertheless, astronomers have managed to discover a new giant radio galaxy using the MeerKAT radio telescope. This galaxy is not only exceptionally large but also quite peculiar, as its physics cannot be easily explained. The study has been published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, reports ScienceAlert.
The size of the new giant radio galaxy, when considering the very long jets of hot plasma emanating from its central supermassive black hole, exceeds 3 million light-years. This makes it more than 30 times larger than our Milky Way galaxy.
This galaxy exhibits unusual properties that are difficult to explain. As a result, the new giant radio galaxy has been named Inkathazo, which means "problem" in one of the indigenous languages of South Africa.

All radio galaxies with supermassive black holes at their centers that expel enormous jets of matter into intergalactic space, detectable via radio waves, possess unique physics. Radio galaxies that, along with their jets of hot plasma, measure over 2 million light-years are classified as giant radio galaxies.
Researchers found that the new galaxy differs from other giant radio galaxies due to its more peculiar physics. For instance, the plasma jets emerging from the black hole do not have a straight trajectory as is typically observed. One of these jets is not straight but rather curved.
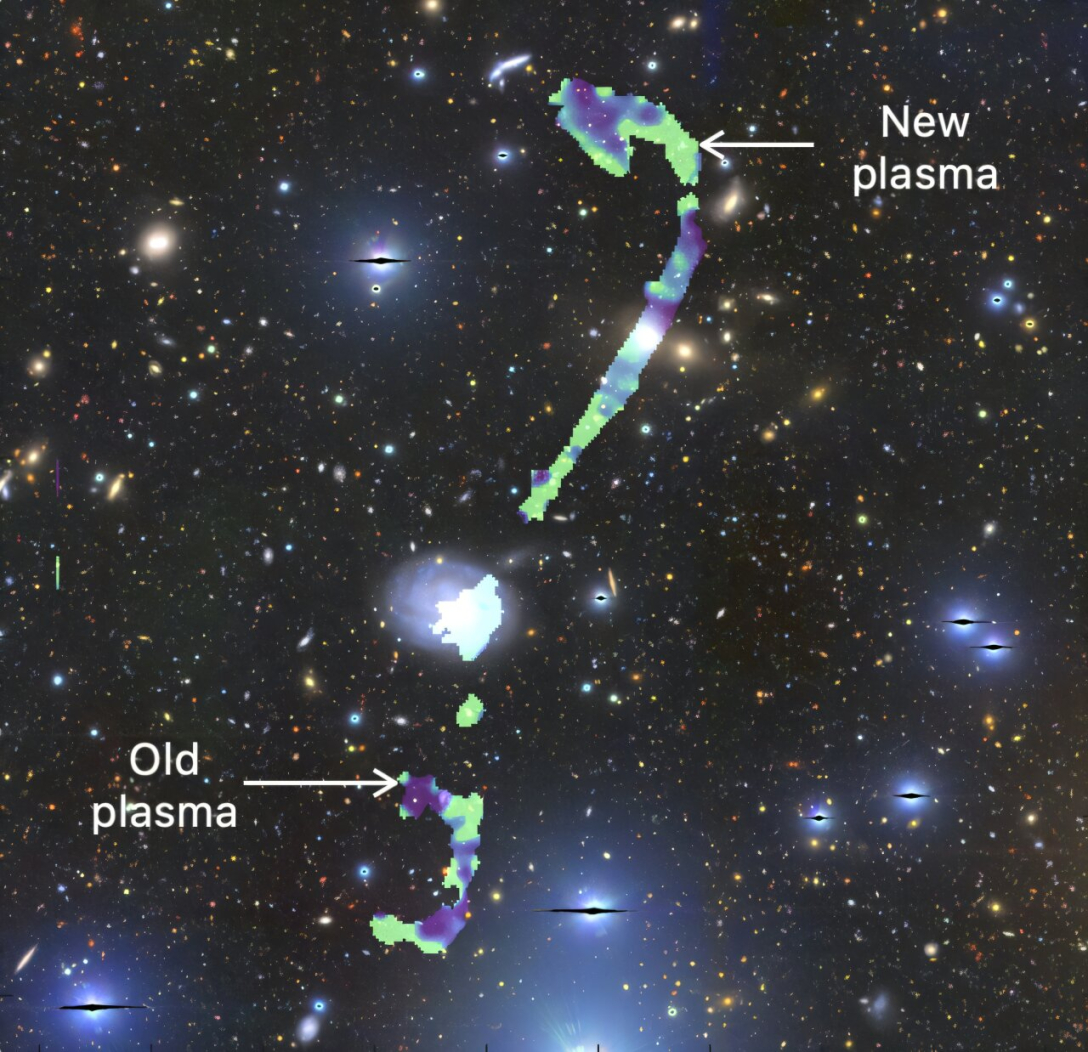
Astronomers also noted that it was surprising for them to find that the new galaxy is located within a galaxy cluster. Such a location should not permit the formation of jets of plasma of this magnitude. Jets of such size are usually found in giant radio galaxies situated in more isolated regions of space.
Scientists have studied the plasma jets and discovered some oddities. Specifically, something within the plasma jets causes electrons to attain unexpectedly high energy levels. This may be related to the interaction of the jets with the surrounding galaxy. The jets do not shoot into relatively empty space but rather into voids between galaxies, where they interact with intergalactic gas. This could be the reason for the electrons' strange behavior.
According to the study’s authors, this new discovery challenges existing theories about the evolution of giant radio galaxies and demonstrates that the complex physics of plasma in these galaxies is still not fully understood.
Giant radio galaxies were previously detected very rarely, but over the past five years, they have been found more frequently thanks to powerful radio telescopes.